Building Your First Nextflow Pipeline: PART 2 - Multiple Samples
Nextflow is a workflow management system designed to simplify the process of writing and executing complex computational workflows. The main advantages of nextflow are:
- Reproducibility: ensures workflows can be run consistently across environments.
- Portability: supports execution on laptops, HPC clusters, cloud (AWS, GCP, Azure), and container platforms (Docker, Singularity).
- Scalability: handles anything from small local runs to massive parallel workloads.
- Modularity: pipelines are built from reusable processes that can be easily combined.
- Container support: seamless integration with Docker, Singularity, and Conda for reproducible software environments.
- Dataflow programming model: channels handle complex data parallelism naturally.
- Error handling & resume: automatic checkpointing allows workflows to resume from failure points.
In the previous post we built a workflow that only processes one sample. The next step is processing multiple samples from a text file.
Sample input file
We generate a tab-separated text file with the relevant information as follows:
1sample_id sample_path chemistry reads1_pat reads2_pat
2pbmc1k rawData/pbmc_1k_v3_fastqs 10xv3 _R1_ _R2_
3pbmc5k_d3 rawData/5k_Human_Donor3_PBMC_3p_gem-x_GEX_fastqs 10xv4-3p _R1_ _R2_
4pbmc5k_d2 rawData/5k_Human_Donor2_PBMC_3p_gem-x_GEX_fastqs 10xv4-3p _R1_ _R2_
Tuple generation
We will follow the strategy of this nextflow pattern to convert each line of the file into a tuple.
1// sample information tsv file
2params.sample_info = 'sample_info.tsv' // path to sample information file
3
4workflow {
5
6 // Load sample information from TSV file
7 sample_info = Channel.fromPath(params.sample_info)
8 .splitCsv(header: true, sep: '\t')
9
10 // Iterate over each sample in the sample info channel
11 sample_info.view { "Sample info: ${it}" }
12}
we include the view command to see the tuples generated from each line of the file and run it as follows
1nextflow run post.2.nf
we get a tupple for each line with the header (first line) as key of the values

Process modification
Next step is to modify the SIMPLEAF_QUANT process to use the values of the tuple instead of a parameter information. I renamed it to QUANT so it is different from the previous post.
1/*
2 * Quantify Gene Expression
3 */
4process QUANT {
5
6 container 'quay.io/biocontainers/simpleaf:0.19.5--ha6fb395_0'
7
8 publishDir "${params.outdir}/quant", mode: 'symlink'
9
10 input:
11 path index_path
12 tuple val(sample_id), val(chemistry), path(reads1_files), path(reads2_files)
13
14 output:
15 path "${sample_id}_quant" , emit: quant_path
16
17 script:
18 def R1_FILES = reads1_files.collect().join(',')
19 def R2_FILES = reads2_files.collect().join(',')
20 """
21 # Download chemistry file
22 wget -O chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json || \
23 curl -o chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json
24
25 # export required var
26 export ALEVIN_FRY_HOME=.
27
28 # prep simpleaf
29 simpleaf set-paths
30
31 # run simpleaf quant
32 simpleaf quant \
33 --reads1 $R1_FILES \
34 --reads2 $R2_FILES \
35 --threads 4 \
36 --index ${index_path}/index \
37 --t2g-map ${index_path}/ref/t2g_3col.tsv \
38 --chemistry ${chemistry} \
39 --resolution cr-like \
40 --unfiltered-pl --anndata-out \
41 --output ${sample_id}_quant
42 """
43}
so basically we modified four parts:
- the input section to receive a tuple
- the publishDir to save the results in a subfolder of the main output folder
- the output section to use the sample_id as prefix of the output folder
- the script section to also use the sample_id as prefix of the output folder
a carefull reader will notice that the input tuple does not have the same structure as the one generated from the tsv file. We need to create a new one in the workflow section to have the list of R1 and R2 files.
Workflow
We use the map function within the channel creation to find the files and then create a new tuple with the required structure. See below the whole workflow section.
1workflow {
2 // Create index channel
3 index = Channel.fromPath(params.index)
4
5 // Load sample information from TSV file
6 sample_info = Channel.fromPath(params.sample_info)
7 .splitCsv(header: true, sep: '\t')
8
9 // Iterate over each sample in the sample info channel
10 sample_info.view { "Sample info: ${it}" }
11
12 // prep for quantification
13 quant_input = sample_info
14 .map { x ->
15 def files_R1 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads1_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
16 def files_R2 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads2_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
17 tuple(x.sample_id, x.chemistry, files_R1, files_R2)
18 }
19 quant_input.view { "Quant input: ${it}" }
20
21 // Alevin-fry quantification
22 quant = QUANT(
23 index,
24 quant_input
25 )
26}
we run it again, I used a version of the sample_info.tsv with only 1 sample to make it faster. As in other posts, I challenge you to build the whole post.2.nf script (solution on the bonus section).
1nextflow run post.2.nf
and we see
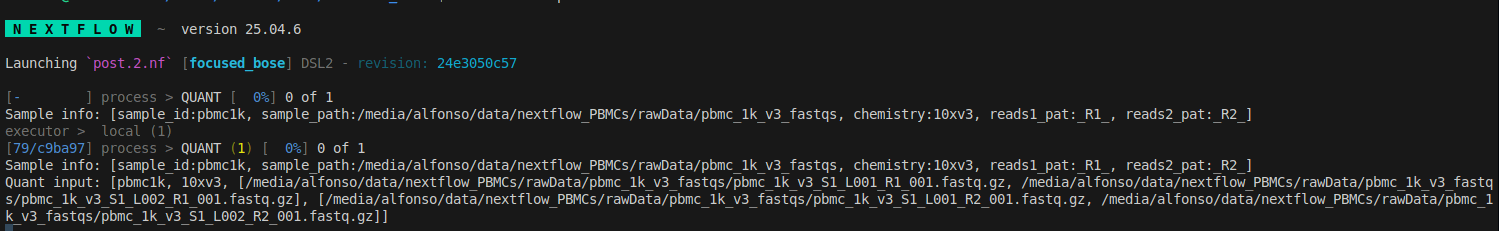
we can see the tuple from the tsv file (Sample info:) and the tuple for the QUANT process (Quant input:), notice the different structure.
When it is done
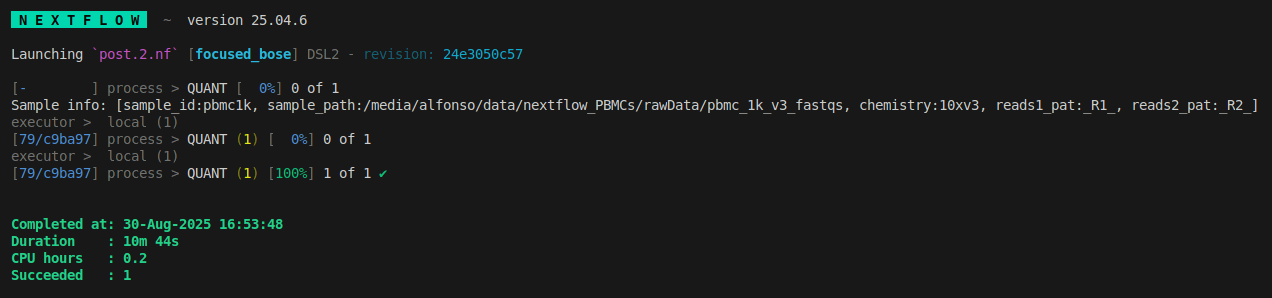
we can check the new results in the output folder, as in the last post we use the -l flag to follow the symlinks
1tree -l results_multisample_quant
1results_multisample_quant
2└── quant
3 └── pbmc1k_quant -> work/79/c9ba979c447e0e0c1d24ac5617843c/pbmc1k_quant
4 ├── af_map
5 │ ├── map_info.json
6 │ ├── map.rad
7 │ └── unmapped_bc_count.bin
8 ├── af_quant
9 │ ├── alevin
10 │ │ ├── quants.h5ad
11 │ │ ├── quants_mat_cols.txt
12 │ │ ├── quants_mat.mtx
13 │ │ └── quants_mat_rows.txt
14 │ ├── collate.json
15 │ ├── featureDump.txt
16 │ ├── gene_id_to_name.tsv
17 │ ├── generate_permit_list.json
18 │ ├── map.collated.rad
19 │ ├── permit_freq.bin
20 │ ├── permit_map.bin
21 │ ├── quant.json
22 │ ├── simpleaf_map_info.json
23 │ └── unmapped_bc_count_collated.bin
24 └── simpleaf_quant_log.json
As you can see, we have the output folder with a sub folder for each sample with the sample_id as prefix. This structure allow to process multiple samples and keep the results separated and ready for downstream analyses.
Full pipeline
Now we have tested the quantificaction from the sample information file, it is time to put all together. We just need to add the index creation process from the first post and connect it to the quantification process.
Hint: you can check the previous script and the last script of the previous post to generate this one (solution in the bonus)
we run the script as usual
1nextflow run post.3.nf
Remember you can use
-resumeflag to avoid rerunning steps if you encounter an error
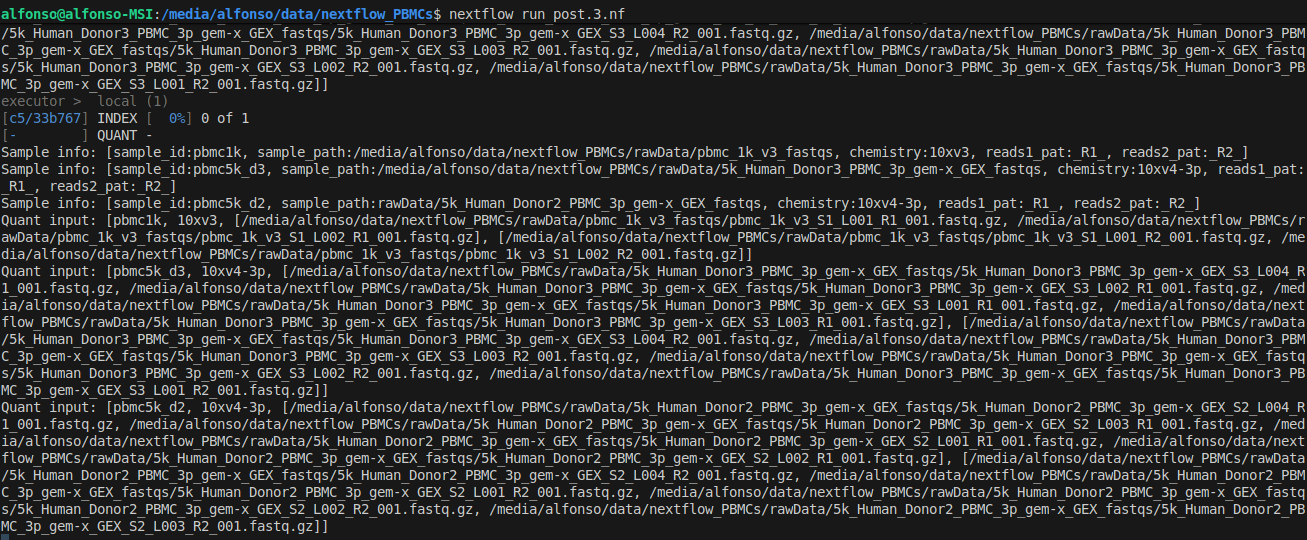
After running the command we see the output of the command views (you may want to remove/comment them once you are sure everything is working fine). We also see the pipeline starts with the index creation.
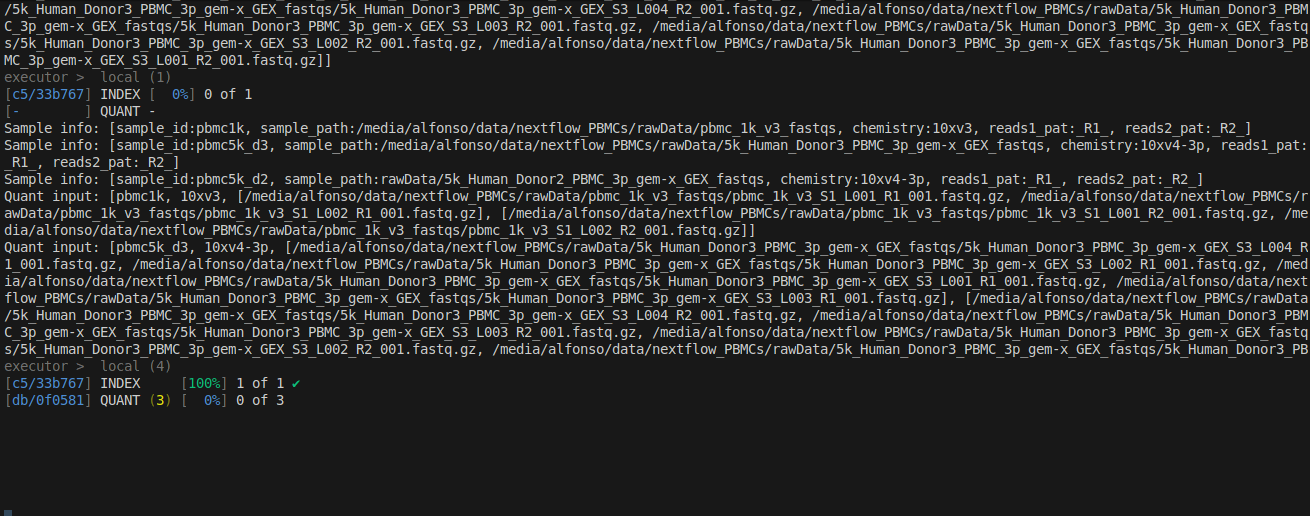
Once the index is done, the INDEX step gets a green check mark and the quantification starts.
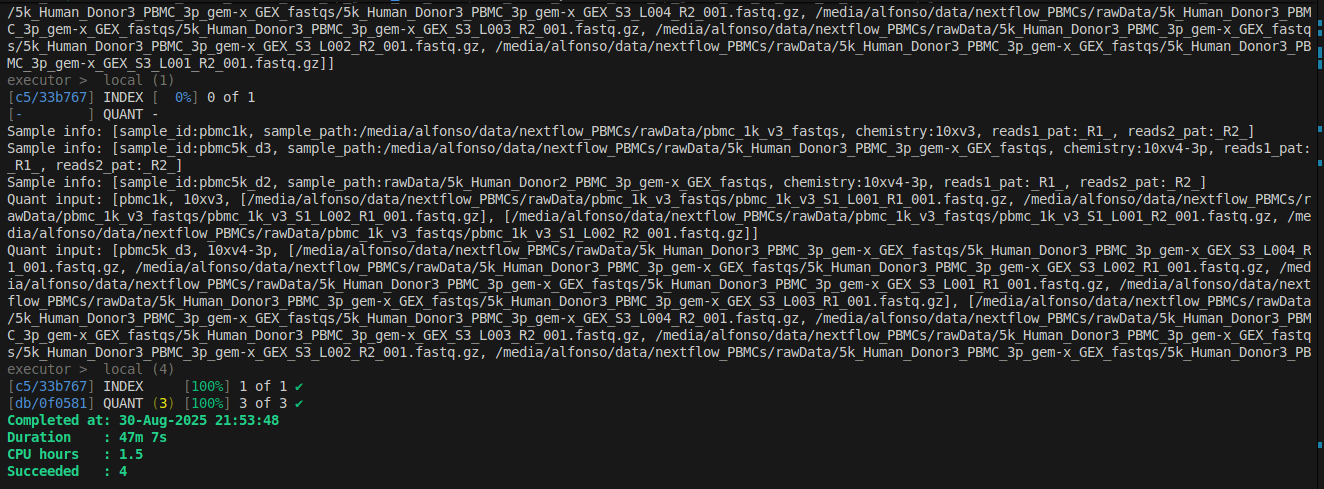
When it is done, we can check the output folder
1tree -l results_full
As discussed before, the quantification of each sample has its own subfolder within the quant folder of the main output folder.
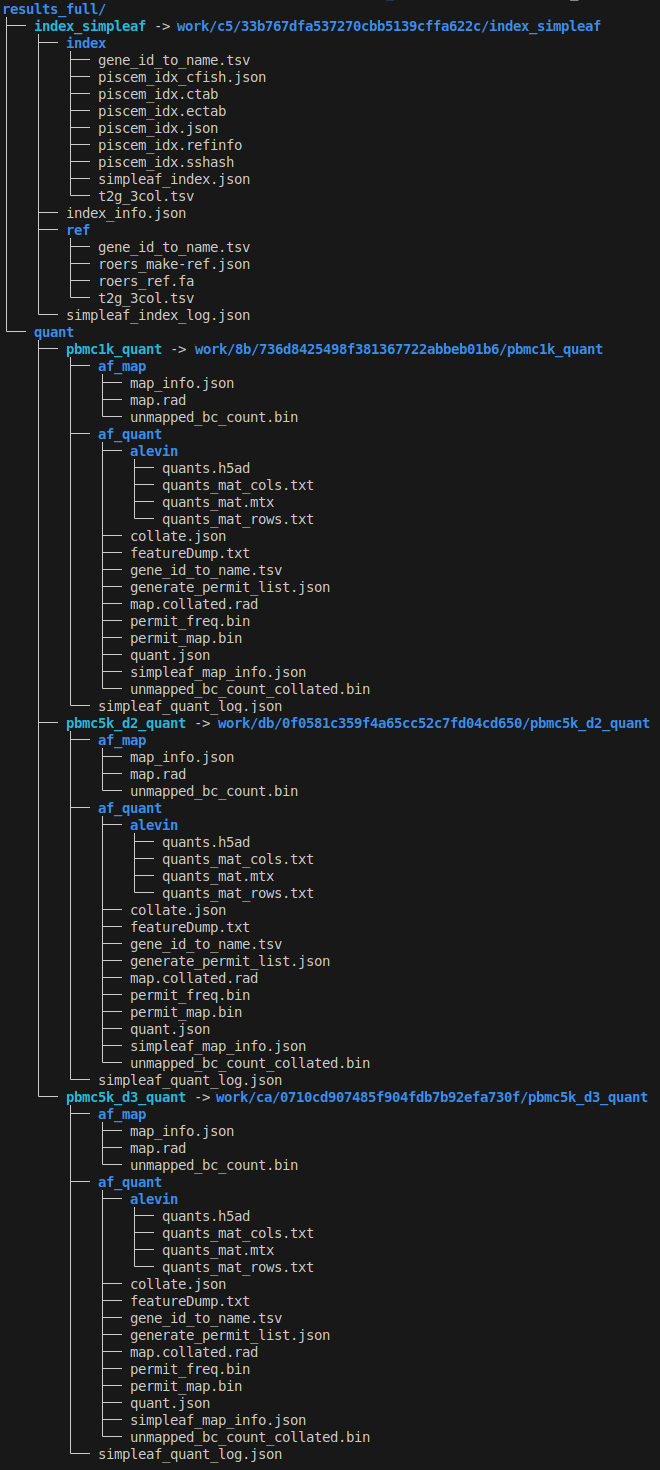
and that's it. Now our workflow can process multiple samples. However, all processes are defined in the main script and parameters are still hard-coded. In the next post we will see how to modularize it make it more flexible and configurable.
BONUS
post.2.nf
Here is the complete post.2.nf script
1// sample information tsv file
2params.index = "${projectDir}/results_simpleaf_index_test/index_simpleaf"
3params.sample_info = 'sample_info_1.tsv' // path to sample information file
4params.outdir = "results_multisample_quant"
5
6
7/*
8 * Quantify Gene Expression
9 */
10process QUANT {
11
12 container 'quay.io/biocontainers/simpleaf:0.19.5--ha6fb395_0'
13
14 publishDir "${params.outdir}/quant", mode: 'symlink'
15
16 input:
17 path index_path
18 tuple val(sample_id), val(chemistry), path(reads1_files), path(reads2_files)
19
20 output:
21 path "${sample_id}_quant" , emit: quant_path
22
23 script:
24 def R1_FILES = reads1_files.collect().join(',')
25 def R2_FILES = reads2_files.collect().join(',')
26 """
27 # Download chemistry file
28 wget -O chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json || \
29 curl -o chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json
30
31 # export required var
32 export ALEVIN_FRY_HOME=.
33
34 # prep simpleaf
35 simpleaf set-paths
36
37 # run simpleaf quant
38 simpleaf quant \
39 --reads1 $R1_FILES \
40 --reads2 $R2_FILES \
41 --threads 4 \
42 --index ${index_path}/index \
43 --t2g-map ${index_path}/ref/t2g_3col.tsv \
44 --chemistry ${chemistry} \
45 --resolution cr-like \
46 --unfiltered-pl --anndata-out \
47 --output ${sample_id}_quant
48 """
49}
50
51workflow {
52 // Create index channel
53 index = Channel.fromPath(params.index)
54
55 // Load sample information from TSV file
56 sample_info = Channel.fromPath(params.sample_info)
57 .splitCsv(header: true, sep: '\t')
58
59 // Iterate over each sample in the sample info channel
60 sample_info.view { "Sample info: ${it}" }
61
62 // prep for quantification
63 quant_input = sample_info
64 .map { x ->
65 def files_R1 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads1_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
66 def files_R2 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads2_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
67 tuple(x.sample_id, x.chemistry, files_R1, files_R2)
68 }
69 quant_input.view { "Quant input: ${it}" }
70
71 // Alevin-fry quantification
72 quant = QUANT(
73 index,
74 quant_input
75 )
76}
post.3.nf
Here is the complete post.3.nf script
1
2/*
3 * Pipeline parameters
4 */
5
6// reference genome path
7params.referenceFASTA = 'reference/refdata-gex-GRCh38-2024-A/fasta/genome.fa'
8params.referenceGTF = 'reference/refdata-gex-GRCh38-2024-A/genes/genes.gtf.gz'
9// sample info
10params.sample_info = 'sample_info.tsv' // path to sample information file
11
12// output directory
13params.outdir = "results_full"
14
15/*
16 * Generate simpleaf index
17 */
18process INDEX {
19
20 container 'quay.io/biocontainers/simpleaf:0.19.5--ha6fb395_0'
21
22 publishDir params.outdir, mode: 'symlink'
23
24 input:
25 path fasta
26 path gtf
27
28 output:
29 path "index_simpleaf", emit : index_path
30
31 script:
32 """
33 # export required var
34 export ALEVIN_FRY_HOME=.
35
36 # set maximum number of file descriptors for temp files
37 ulimit -n 2048
38
39 # prep simpleaf
40 simpleaf set-paths
41
42 simpleaf index \
43 --output index_simpleaf \
44 --fasta ${fasta} \
45 --gtf ${gtf} \
46 --threads 4 \
47 --work-dir ./workdir.noindex
48 """
49}
50
51/*
52 * Quantify Gene Expression
53 */
54process QUANT {
55
56 container 'quay.io/biocontainers/simpleaf:0.19.5--ha6fb395_0'
57
58 publishDir "${params.outdir}/quant", mode: 'symlink'
59
60 input:
61 path index_path
62 tuple val(sample_id), val(chemistry), path(reads1_files), path(reads2_files)
63
64 output:
65 path "${sample_id}_quant" , emit: quant_path
66
67 script:
68 def R1_FILES = reads1_files.collect().join(',')
69 def R2_FILES = reads2_files.collect().join(',')
70 """
71 # Download chemistry file
72 wget -O chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json || \
73 curl -o chemistries.json https://raw.githubusercontent.com/COMBINE-lab/simpleaf/dev/resources/chemistries.json
74
75 # export required var
76 export ALEVIN_FRY_HOME=.
77
78 # prep simpleaf
79 simpleaf set-paths
80
81 # run simpleaf quant
82 simpleaf quant \
83 --reads1 $R1_FILES \
84 --reads2 $R2_FILES \
85 --threads 4 \
86 --index ${index_path}/index \
87 --t2g-map ${index_path}/ref/t2g_3col.tsv \
88 --chemistry ${chemistry} \
89 --resolution cr-like \
90 --unfiltered-pl --anndata-out \
91 --output ${sample_id}_quant
92 """
93}
94
95workflow {
96
97 // define input files & variables
98 fasta = file("${params.referenceFASTA}") // refrence fasta
99 gtf = file("${params.referenceGTF}") // annotation GTF
100
101 // Load sample information from TSV file
102 sample_info = Channel.fromPath(params.sample_info)
103 .splitCsv(header: true, sep: '\t')
104
105 // Iterate over each sample in the sample info channel
106 sample_info.view { "Sample info: ${it}" }
107
108 // INDEX creation
109 index = INDEX(
110 fasta,
111 gtf
112 )
113
114 // prep for quantification
115 quant_input = sample_info
116 .map { x ->
117 def files_R1 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads1_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
118 def files_R2 = file("${x.sample_path}/*${x.reads2_pat}*", checkIfExists: true)
119 tuple(x.sample_id, x.chemistry, files_R1, files_R2)
120 }
121 quant_input.view { "Quant input: ${it}" }
122
123 // Alevin-fry quantification
124 quant = QUANT(
125 index.index_path,
126 quant_input
127 )
128}